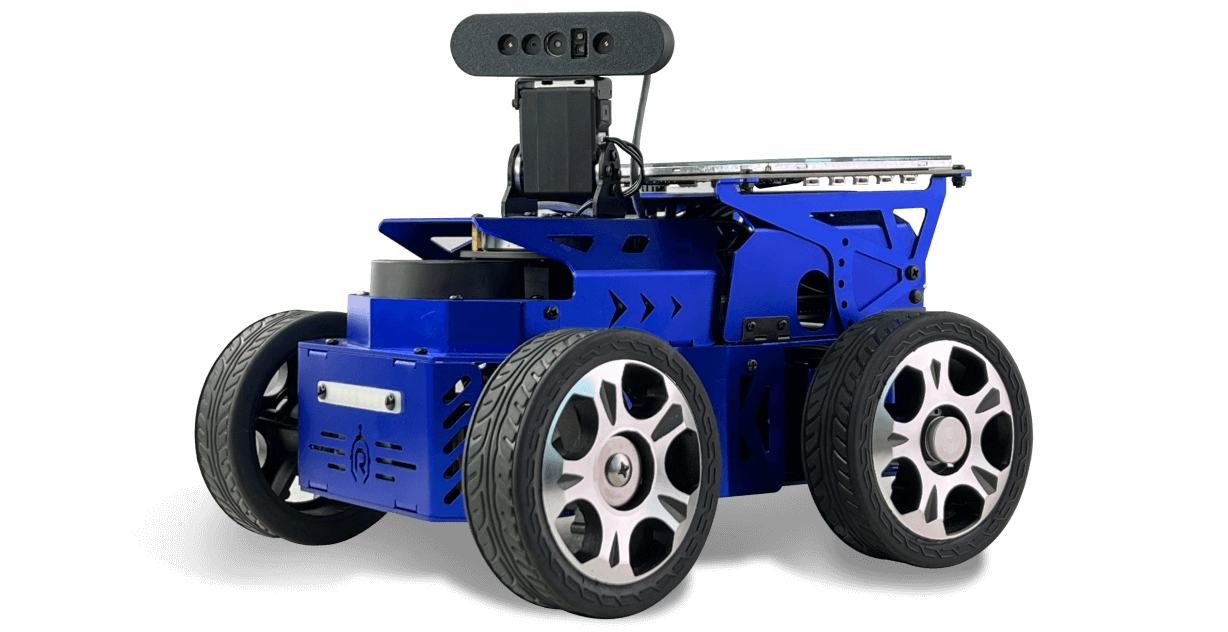
- Product images

ROS Hunter Ackerman autonomous navigation robot is designed by XiaoR Technology for in-depth exploration of unmanned driving and robot navigation technology. It is based on NVIDIA Jetson Nano and uses the advanced ROS2 framework. It is a professional-grade autonomous navigation car. The chassis of the car adopts the Ackerman steering structure, which is derived from the standard steering system of modern cars. It can accurately simulate the guidance mechanism of real vehicles and is particularly suitable for research scenarios that require high simulation.
In addition, the robot is equipped with a series of high-performance hardware components, including but not limited to NVIDIA Jetson Nano main control board, high-torque encoder reduction motor, advanced laser radar, 3D depth camera, 7-inch LCD display and programmable cool lights. The integration of these components enables the robot to perform complex tasks such as precise robot motion control, mapping and navigation path planning using ROS SLAM algorithm, deep learning and visual interaction.
In order to improve the user experience, ROS Hunter supports multiple control methods, including mobile phone APP, virtual machine RVIZ, PS4 handle, etc. Users can easily switch between mapping and navigation modes. The robot is designed to allow users to quickly and intuitively enter the development process, so it also provides a complete set of ROS courses, covering technical information, functional source code, documents and explanation videos to help users quickly master the development and application of ROS robots.
In addition, ROSHunter is equipped with the "ROS human-computer interaction system" independently developed by XiaoR Technology, which can provide real-time feedback on the robot's operating status, program execution (such as mapping, navigation and map saving, etc.) and system information viewing, further enhancing the robot's user interaction ability and practicality. This autonomous navigation robot is not only an ideal choice for technology enthusiasts and researchers, but also an excellent tool for advanced technology teaching in the field of education.
Key technologies: C++/Python/ROS2/SLAM autonomous navigation/3D depth vision/autonomous driving
Overall product parameters
|
Body structure parameters |
||||||
|
Size |
294*234*233mm |
|||||
|
Weight |
3.4kg |
|||||
|
Material |
Metal aluminum alloy |
|||||
|
Craftsmanship |
Anodized |
|||||
|
Color |
Blue |
|||||
|
Moving mechanism |
Ackerman steering structure |
|||||
|
Speed |
0.8m/s |
|||||
|
Auxiliary control board interface performance parameters |
||||||
|
Main control chip
|
Chip model |
STM32F103RCT6 |
||||
|
Operating voltage |
3.3V |
|||||
|
Operating frequency |
72MHZ |
|||||
|
Sensor interface
|
Number of interfaces |
3 |
||||
|
Interface type |
4PIN-ZH1.5 |
|||||
|
Voltage |
5V |
|||||
|
Current |
200mA |
|||||
|
Communication method |
UART |
|||||
|
Servo interface
|
Number of interfaces |
2 |
||||
|
Interface type |
3PIN-PH2.0 |
|||||
|
Voltage |
12.6V |
|||||
|
Current |
8A |
|||||
|
Communication method |
UART |
|||||
|
Motor interface
|
Number of interfaces |
4 |
||||
|
Interface type |
6PIN-PH2.0 |
|||||
|
Voltage |
12.6V |
|||||
|
Rated current |
2A |
|||||
|
Peak current |
3A |
|||||
|
Onboard USB interface |
Number of interfaces |
2 |
||||
|
Interface type |
4PIN-ZH1.5 |
|||||
|
Voltage |
5V |
|||||
|
Rated current |
1.5A |
|||||
|
Communication method |
USB |
|||||
|
Peripheral electronic devices |
||||||
|
Display screen |
Model |
HDMI Display high-definition display |
||||
|
Camera |
Model |
Binocular depth camera, 1080P |
||||
|
Motor parameters |
Reduction ratio |
1:30 |
||||
|
No-load current |
1.2A |
|||||
|
Locked-rotor current |
3.5A |
|||||
|
Rated torque |
0.3kg.cm |
|||||
|
Locked-rotor torque |
6.0kg.cm |
|||||
|
Servo parameters |
Drive voltage |
6V-12V |
||||
|
No-load current |
180mA |
|||||
|
Locked-rotor current |
2.7A |
|||||
|
Communication method |
UART |
|||||
|
Communication frequency |
1Mbps |
|||||
|
Development software |
Programming language/programming tool |
C language, Python, IAR |
||||
|
Control system |
XR-GUI |
XR-GUI human-computer interaction system |
||||
|
Main control board parameters |
Main chip |
Quad-core ARM quad-core A57; 128-Maxwell architecture |
||||
|
Interface |
USB2.0, 100M network port, serial port, 40PIN I/O port |
|||||
|
WIFI transmission distance |
About 80M under 5dBi conditions |
|||||
|
Compatible video format |
Mjpeg, YUV |
|||||
|
Control method |
2.4G handle/APP/virtual machine RVIZ |
|||||
|
PTZ parameters |
Degree of freedom |
Two degrees of freedom |
||||
|
Servo |
S015M metal axis |
|||||
Shipping list
The product is shipped as a finished product, the product list is as follows:
|
Accessory name |
Quantity |
|
Ackerman robot chassis |
1 |
|
Jetson Nano main control board |
1 |
|
PWR.4RPL robot driver board |
1 |
|
Encoder motor |
4 |
|
5DBi patch antenna |
2 |
|
Binocular depth HD camera |
1 |
|
10000mAh lithium battery |
1 |
|
Charger |
1 |
|
Hardware package |
1 |
|
2-DOF gimbal |
1 |
|
XR-S002 laser radar |
1 |
|
2.4G remote control handle |
1 |
|
Instruction manual |
1 |
Product Functions
|
Ackerman travel mode |
The car adopts the Ackerman travel mode. Through the reasonably designed steering mechanism and steering rod/pull rod, and the application of the Ackerman principle, the differential steering of the inner and outer wheels when the vehicle turns is realized, thereby improving the robot's controllability and stability. |
|
2-DOF PTZ gimbal |
The robot is equipped with a high-performance 2-DOF PTZ gimbal, which enables the robot to achieve up and down, left and right directions and look around and upward, thereby expanding the robot's viewing angle rotation range. |
|
WIFI wireless remote control |
After the car is turned on, it generates a WiFi signal. The mobile phone or tablet can connect to the car through WiFi and control it with a dedicated APP. |
|
2.4G wireless handle remote control |
The car is compatible with 2.4G wireless handle real-time remote control, supports handle control of the robot, and the control link is stable; |
|
SLAM mapping and navigation |
With the XR-ROS human-computer interaction system, the SLAM laser radar mapping and automatic navigation functions can be realized through the APP or virtual machine, and obstacles are encountered during the journey. Automatically plan a new route to avoid. |
|
3D deep vision mapping and navigation |
Use the RTAB SLAM algorithm, combined with visual and radar information, to build a three-dimensional color map. On this basis, the robot can realize autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance in the map, and support global relocation and autonomous positioning functions. |
|
Opencv visual line patrol |
The camera machine vision can realize autonomous judgment of the black line on the road surface and follow the black line to achieve tracking. |
|
Machine vision processing |
The built-in visual development framework can realize functions such as face detection, edge detection, augmented reality, and color recognition. |
Product information
Provide detailed electronic files and source code to assist learning, and provide supporting practical training materials with no less than 11 categories and 74 courses. The content covers from understanding ROS to fully mastering ROS-SLAM development and artificial intelligence technology. Knowledge points include: Linux system application, wireless remote control technology, single-chip microcomputer technology, Internet of Things sensor application technology, SLAM mapping and navigation technology, ROS robot application technology, program code open source, and support for secondary development.
Course List
Catalog
Chapter 1 Overview of ROS2
Chapter 2 Introduction to the ROS2 SLAM Car Architecture
- Introduction to the robot motherboard and driver board
- Description of the overall framework
Chapter 3 Basic Operations
- APP installation and operation
- Virtual machine installation and keyboard operation
- Network settings between the robot and the computer
- Keyboard control on the virtual machine
Chapter 4 Secondary Development Environment Construction
- Secondary Development Software Installation and Use
1.1 Backup Image
1.2 Restore Image
- Introduction to SSH and Two Remote Login Methods
2.1 Using SSH in Linux/Terminal
2.2 Using SSH in Windows
- ROS2 Car Source Code
- System Architecture
Chapter 5 Introduction to ROS Basics
- Installation of ROS2 Framework
- Introduction to ROS2 Architecture
- Introduction to ROS2 Communication Mechanism
- Creation of ROS2 Application Workspace and Function Package
4.1 Create ROS2 Application Workspace
4.2 Create ROS2 Function Package
4.3 Compilation of ROS2 function package
- Introduction to ROS2 nodes
5.1 ros2 run
5.2 ros2 node list
5.3 remapping
5.4 node information
- Introduction to launch files and commands in ROS2
6.1 Introduction to launch files in ROS2
6.2 Common launch file writing methods
6.3 Create a single-node launch file
6.4 Create a multi-node launch file
- Introduction to RVIZ2 visualization platform
- Introduction to xros
- Introduction to xrosmanager2
Chapter 6 Introduction to SLAM mapping and navigation
- Introduction to SLAM
1.1 Development history of SLAM
1.2 Typical application areas of SLAM
1.3 SLAM framework
1.4 SLAM classification (sensor-based SLAM classification)
- Common SLAM algorithms
2.1 Hector SLAM algorithm
2.2 Gmapping algorithm
2.3 cartographer algorithm
- SLAM mapping and map saving operations
3.1 Laser SLAM mapping operations
3.2 Save map operations
3.3 Visual mapping operations
- Navigation introduction
4.1 Nav2 (2D navigation)
4.2 rtabmap visual navigation
- Robot underlying driver
Chapter 7 AI artificial intelligence technology
- Introduction to AI artificial intelligence technology
- AI artificial intelligence technology case analysis
2.1 Edge detection
2.2 Aruco augmented reality
2.3 Face recognition
2.4 Color recognition
2.5 Visual line patrol
- Simple follow function case
3.1 Radar follow
3.2 Visual tracking
3.3 Visual line patrol